When you look around your room electricity is everywhere. Powering your lights, your phone, air conditioner, your computers and more. Electricity is also in nature, for example electricity is present throughout natural phenomena’s. Electricity takes many different forms, in this website we will focus on current electricity: this is the stuff that powers our electronic gadgets. Electricity is simply defined the flow of electric charge, however, this only scratches the surface of what electricity is, there is so much more, like where do the charges come from? How do we move them? Where do they move to? How does electric charge power things? and much more.
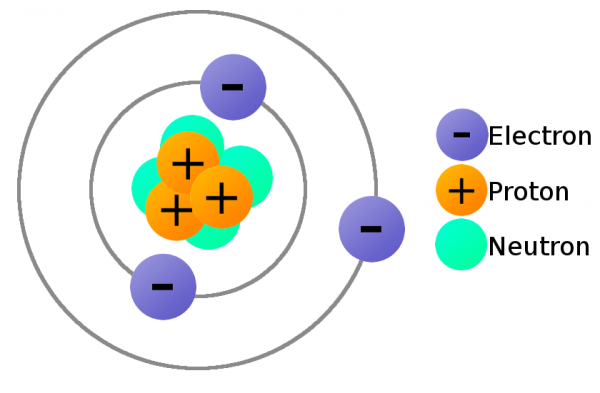
Atoms are the building block of matter. But even the atom is not small enough for us to be able to explain the workings of electricity. We need to go smaller than this and look at what makes up atoms: protons, neutrons and electrons. Each atom also has a nucleus, located in the centre, which contains protons and neutrons. The electrons move around the nucleus. Electric charge is the physical property of matter that causes it to experience a force when placed in an electromagnetic field. Electric charges can be positive or negative and are never created or destroyed. An electric current is a flow of electric charge. This current flows as the electrons (negatively charged electricity) that the charge carries in a circuit flow in the opposite direction of the conventional current (moving in the same direction as the positive charge flow). The electrons are the main component of electricity, without them electricity is not possible. The atom’s electrons aren’t all forever bound to the atom. The electrons on the outer orbit of the atom are called valence electrons. With enough outside force these electrons are able to escape their orbit and become free. Free electrons allow us to move charge, this is the main idea of electricity.
Electric charge is the physical property of matter that causes it to experience a force when placed in an electromagnetic field. There are two types of electric charges: positive and negative. Charge carriers move charge. Electrons are negatively charged atoms, meaning they carry a negative charge, protons are positively charge atoms, meaning they carry a positive charge and neutrons have zero charge, they are neither positively charged, nor negatively charge. Although electrons and protons carry different types of charge, they both carry the same amount, we can see this in the diagram below.